Vibe Coding with Specification
Over the past few days, I decided to revisit and improve ankihelper, an Android application for creating Anki flashcards. Originally developed by mmjang, development stopped in 2021. Despite this, I still use it to create flashcards for new words, so continuing its development seemed worthwhile. However, as someone without much experience in software development, I found myself struggling with basic principles. That’s when I turned to AI programming as my last resort. Last year, I managed to update the codebase using zed, which took me a week to make it run on Android 11 and above, but it’s still not perfect.
Writing Specifications for Code
Last month, I came across The New Code — Sean Grove, OpenAI on Twitter, and I became obsessed with the idea. The concept is simple: create a specification to guide AI in implementing features for you. It’s feasible, so I started working on it.
Since I’ve used AnkiHelper for a long time, I know what features I need. Here’s my plan:
- Fix permission requests on first launch (new Android versions changed something, and it can’t request permission now)
- Update the UI to Material 3
- Popup Edit Mode Design Documentation
- Add LLM feature (sometimes the built-in dictionary doesn’t have a word, so we can use LLM as a dictionary)
- Remove unused dictionaries
- Other UI improvements
Choosing Code Tools
CLI tools
-
Commercials
-
Opensource
-
orchestrator
claude code
This year, new code tools have emerged rapidly. Anthropic released claude, a command-line tool for coding, which is a game changer. OpenAI followed with Codex, Google released Gemini CLI, and Qwen team introduced qwen-code, among others.
Since I live in China, Qwen is my best choice. It may not have the best performance, but it’s free for developers, offering 2,000 requests per day with decent results.
make sure to configure context7 mcp server,
-
using nvm
Terminal window curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bashnvm install 22nvm alias default 22 -
installation agent tools
Terminal window npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-codeor
Terminal window npm install -g @qwen-code/qwen-code@latestor
Terminal window npm install -g @google/gemini-cli -
~/.qwen/settings.json
{"mcpServers": {"context7": {"httpUrl": "https://mcp.context7.com/mcp","headers": {"CONTEXT7_API_KEY": "xxx"}},"deepwiki":{"httpUrl": "https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp"}},"selectedAuthType": "qwen-oauth"}I’d like to use
claude, but it’s a bit expensive and requires some extra steps to access. now domestic comanpy also support cluade, I requested to use with claudeTerminal window claude --dangerously-skip-permissions -
~/.claude/settings.json
-
zhipu
{"env": {"ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL": "https://api.z.ai/api/anthropic", // or https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/anthropic"API_TIMEOUT_MS": "3000000","ANTHROPIC_DEFAULT_HAIKU_MODEL": "glm-4.5-air","ANTHROPIC_DEFAULT_SONNET_MODEL": "glm-4.6","ANTHROPIC_DEFAULT_OPUS_MODEL": "glm-4.6","ANTHROPIC_API_KEY": "xxx",}} -
deepseek
{"env": {"ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL":"https://api.deepseek.com/anthropic","ANTHROPIC_API_KEY": "xxx","ANTHROPIC_MODEL": "deepseek-chat","ANTHROPIC_SMALL_FAST_MODEL": "deepseek-chat"}} -
moonshot
{"env": {"ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL":"https://api.moonshot.ai/anthropic","ANTHROPIC_API_KEY": "xxx","ANTHROPIC_MODEL": "kimi-k2-0905-turbo-preview","ANTHROPIC_SMALL_FAST_MODEL": "kimi-k2-0905-turbo-preview"}} -
add some environment variables,
MAX_MCP_OUTPUT_TOKENS: this will increase the allowed token from MCP server, sometimes MCP tools (such as figma) will respond with large content which is essential"MAX_MCP_OUTPUT_TOKENS": 100000CLAUDE_CODE_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS: max output claude code"CLAUDE_CODE_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS": 50000- “ENABLE_TOOL_SEARCH”: “true”,
- “CLAUDE_CODE_EXPERIMENTAL_AGENT_TEAMS”: “0”
-
set default mode
..."permissions": {"defaultMode": "bypassPermissions","allow": ["mcp__pencil"]},...
-
-
onboarding
- ~/.claude.json
"hasCompletedOnboarding": true, make sure claude will not ask to onboard again.Terminal window jq -r '.hasCompletedOnboarding' ~/.claude.jsontrue
- ~/.claude.json
-
status line
- CCometixLine
- ccstatusline
- configure status line show more info, especially for context, claude will compact the context when the context reached about 95%,
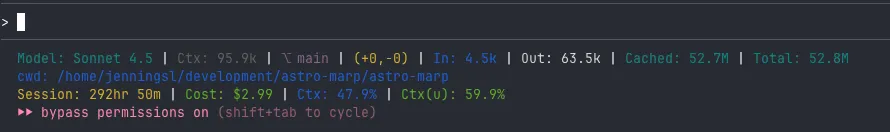
- configure status line show more info, especially for context, claude will compact the context when the context reached about 95%,
-
memory management
- nowledge mem
-
first install nowledge app on your mac, it will start
mcpserver locally -
install the plugins in claude code
/plugin marketplace add nowledge-co/community/plugin install nowledge-mem@nowledge-community -
add mcp server to claude code
Terminal window claude mcp add --transport http nowledge-mem http://localhost:14242/mcp --scope useror
Terminal window claude mcp add --transport http nowledge-mem http://localhost:14242/mcp -
save/retrieve the memeory via slash commands or via mcp server
- slash command
/saveor/sum - use mcp tools
- slash command
-
- specstory: Turn your AI development conversations into searchable, shareable knowledge.
- nowledge mem
-
CLAUDE.mdinit
CLAUDE.mdusing zcf -
model switch/apihub tools
-
Claude Relay Service: 自行搭建Claude API中转服务,支持多账户管理
-
axonhub: is an all-in-one AI development platform that provides unified API gateway, project management, and comprehensive development tools. It offers OpenAI, Anthropic, and AI SDK compatible API layers, transforming requests to various AI providers through a transformer pipeline architecture. The platform features comprehensive tracing capabilities, project-based organization, and integrated playground for rapid prototyping, helping developers and enterprises better manage AI development workflows.
-
quotio: Quotio is a native macOS application for managing CLIProxyAPI - a local proxy server that powers your AI coding agents. It helps you manage multiple AI accounts, track quotas, and configure CLI tools in one place.
-
AIClient-2-API:A powerful proxy that can unify the requests of various client-only large model APIs (Gemini CLI, Antigravity, Qwen Code, Kiro …), simulate requests, and encapsulate them into a local OpenAI-compatible interface.
-
AntigravityManager: Professional multi-account manager for Google Gemini & Claude AI
-
add mcp server
following the commands to add mcp tools to claude, you can use same command to add them in
qwen,gemini, just replaceclaudewith the desired command-
mcp registry
-
context7
create context7 api on https://context7.com/dashboard
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t http context7 https://mcp.context7.com/mcp --header "CONTEXT7_API_KEY: YOUR_API_KEY" -
deepwiki
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t http deepwiki https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp -
chrome-devtools-mcp lets your coding agent (such as Gemini, Claude, Cursor or Copilot) control and inspect a live Chrome browser
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t stdio chrome-devtools npx chrome-devtools-mcp@latestit can check and page, get screenshot to find if the page behaves like what you want
-
figma, use official mcp, see https://www.figma.com/mcp-catalog/
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t http figma-remote-mcp https://mcp.figma.com/mcpadd more rules to
~/.claude/CLAUDE.mdfor user scope and also project levelCLAUDE.md, especially https://developers.figma.com/docs/figma-mcp-server/add-custom-rules#rules-to-ensure-consistently-good-output -
playwright
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t stdio playwright npx @playwright/mcp@latest -
exa: create api keys on https://dashboard.exa.ai/api-keys
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t http exa "https://mcp.exa.ai/mcp" --header "EXA_API_KEY: xxx" -
astro mcp
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user --transport http astro-docs https://mcp.docs.astro.build/mcp -
time mcp
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t stdio time-mcp npx time-mcpadd a rule to
~/.claude/CLAUDE.mdor projectCLAUDE.mdwhich make claude also find the latest materials when search/find documents/materials## Time MCP rules (MUST follow)- in every prompt, add the current date and time as an extra info for context -
Claude Code with GLM coding plan to process images with its MCP(only work when claude code with glm 4.6 model)
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user --env Z_AI_API_KEY=api_key Z_AI_MODE=ZAI -t stdio zai-mcp-server npx "@z_ai/mcp-server" -
stackoverflow
Terminal window claude mcp add -s user -t stdio stack-mcp-server npx mcp-remote https://mcp.stackoverflow.com
-
-
some other configs for claude, may still need more configuration
- zcf
- spec-kit
- ruler: create
CLAUDE.md - dotclaude: multiple config, maybe only reference
CLAUDE.md - claude-code-templates: also maybe only reference
CLAUDE.md - CodeRabbit CLI: Free AI code reviews in your CLI
Getting Started
Initially, i just prompt for every spec
In the codebase, I created a specification directory. For each feature, I made a subdirectory for the AI to generate the spec.
For each feature, I simply describe the requirements, including UI layout (I don’t use Figma, just words), functions, and input/output formats.
Please create a new subdirectory under specifications for the following features/fixes:- fix issue 1- fix issue 2- implment feature 1
<add more description or requirements here>
Follow this systematic approach:1. Research Phase: Conduct comprehensive research including: - Best practices and design patterns - Official documentation and API references - Informative blog posts and tutorials - Relevant GitHub issues and discussions - Performance considerations and edge cases - Use MCP tools such `websearch`, `exa`, `context7`, `deepwiki` to find all kinds of materials - <other specific documents, such api and documents for a lib/package>2. Specification Phase: Create comprehensive documents: - Technical specification with architecture decisions - Detailed implementation plan with milestones - Task list with prioritized subtasks - Add a final task to commit and push changes
3. after specification is created, do a second validation check
4. Execution Phase: Create and coordinate three specialized sub-agents in parallel:
Development Agent responsibilities: - Generate code following established patterns - Apply linting and formatting - Build after each code generation - Document implementation choices
Testing Agent responsibilities: - Validate builds run without errors - Execute CodeRabbit analysis with `coderabbit --prompt-only`, let it run as long as it needs (run it in the background) and fix any issues. - Write and run unit/integration tests - Document edge cases and test coverage - Use MCP tools to conduct additional testing wherever possible - For website pages project, use MCP tools such as `playwright` and `chrome-devtools` to test and validate the website pages: exercise inputs, checks, buttons, and navigation; do not invoke npm or playwright directly
Documentation Agent responsibilities: - Track implementation progress - Create implementation-summary.md with: * Technical decisions rationale * Code structure overview * Challenges encountered and solutions * Performance metrics
5. Coordination: Progress through tasks sequentially: - Assign next task only after previous completion - Stop for human review at major checkpoints - Ensure all agents work with consistent context - Maintain a single source of truth for specifications
Upon completion of all tasks, commit with descriptive message and push changes to repository.Update: on 2025-11-07
In the last couple of days, i improved the process by creating a cumstom commands, which fit call these process into a slash command, each time i just supply the required error info, or feature requirements, and additional documents
i think this is not perfect, i will create more process for different project with different command
create file under ~/.claude/commands/dev/
---name: dev: impl-and-fixdescription: fix the error or implement new functions during the developmentcategory: dev---whenever user ask you to do following things- fix a issue or bug- fix build warnings or errors- implement a new feature- improve a feature- improve the performance- resolve the deprecation- refactor the code
Follow this systematic approach:
1. Analyze the information user provided, identify which specification to - If found related specs, one or more choices, ask user to confirm - If not found any related specs, create one sub directory under specification, the name pattern of the sub directory is [index(number)]-[feature name of fix name] - Never create documents under project root or directly under specification, documents must be created under sub directory of specification - In the following phases, if the phases have output files, they should always be stored using in the sub specification directory [index(number)]-[feature name or fix name], with the document named [index(number)]-[document name].md
2. Clarify the requirements - If it is a feature, ask questions like following but not limited: - If it has design, such Figma design, if yes, ask user to provide - What technical stack will be used - What programming languages it will use - What is the structure - You can also find the latest best practices question/clarification and ask user to provide - what programming languages will be used
- If it is a bug fix, ask questions like following but not limited: - What environment, mobile or desktop - OS - Browser - Screenshot with error message - Logs (build logs, runtime logs, debug logs) - You can also find the latest best practices question/clarification and ask user to provide
3. Research Phase: Conduct comprehensive research including: - When doing research, add current time from time MCP to context - Best practices and design patterns - Official documentation and API references - Informative blog posts and tutorials - Relevant GitHub issues and discussions - Performance considerations and edge cases - Use MCP tools like `websearch`, `exa`, `context7`, `deepwiki` to find materials - Use all available skills - Use specialist agents like search-expecialist, search-specialist - Find latest documents for latest versions of libraries/tools for development - Create one file: - Research report
4. Debug Phase: Conduct comprehensive research including (apply to error or bug): - Analyze the codebase based on information from the Research Phase - If you need to find any pattern in the code, you can use the `ast-grep` skill to identify and locate it - Propose root cause analysis - Utilize multiple skills - use specialist agents like debugging specialist, - Create files: - Debug analysis document
5. Assessment Phase: Assess the current code including architecture, code style, and frameworks: - Evaluate if current architecture is optimal compared to best practices - Determine if we are using the latest code rules and formatting standards - Check if we are using the latest packages, libraries, and frameworks - Identify if there are better options available - Create files: - Assessment document
6. Specification Phase: Create comprehensive documents: - Technical specification with architecture decisions by referencing the documents created by previous phases - Following the api documents, make sure use aligned api specification - Detailed implementation plan with milestones - Task list with prioritized subtasks - Add a final task to commit and push changes - Use specialist agents like backend-architect, database-architect, cloud-architect, and other relevant specialists to help create the specification - Create 3 files: - One specification - One implementation plan based on the specification - One task list broken down from the implementation plan7. Review Phase: Review the specification, plan, and task list:
- Ensure they are aligned with our requirements - Verify they follow current best practices - Confirm they include proper code constraints for industrial standards and best practices - Validate the specification is executable and testable
8. Execution Phase: Create and coordinate three specialized sub-agents simultaneously, running in parallel using `subagent-driven-development` skill:
Prohibit to pause or stop during this phase. If there are multiple implementation options, always choose the one that continues to implement all tasks, unless it is not feasible or there is a better solution.
During the execution phase, when you need to locate specific code patterns for modification (add/delete/edit operations), utilize the `ast-grep` skill to efficiently search and filter through the codebase.
Development Agent responsibilities: - Generate code following established patterns - Apply linting and formatting - Build after each code generation - Document implementation choices - Make sure to use the latest libraries and tools - Ensure no build warnings or errors exist; all issues must be fixed, not suppressed - Organize code in modular, loosely-coupled components - Maintain consistent data schemas across the codebase - Employ specialist agents like rust-pro, backend-developer, frontend-developer, mobile-developer, ios-developer, and other relevant specialists
Testing Agent responsibilities: - Validate builds run without errors - Execute CodeRabbit analysis with `coderabbit --prompt-only`, let it run as long as it needs (run it in the background) and fix any issues - Write and run unit/integration tests - Document edge cases and test coverage - Use MCP tools to conduct additional testing wherever possible - For website pages project, use playwright-skills and MCP tools such as `playwright` and `chrome-devtools` to test and validate the website pages: exercise inputs, checks, buttons, and navigation; do not invoke npm or playwright directly - Employ specilist agent like superpowers:code-reviewer and other relevant specialists
Documentation Agent responsibilities: - Track implementation progress - Create implementation-summary.md with: * Technical decisions rationale * Code structure overview * Challenges encountered and solutions * Performance metrics - Employ specialist agents like documentation-expert and api-documenter and other relevant specialists
After execution, in addition to the code and test, create one more file: - One implementation summary
9. Coordination: Progress through tasks sequentially: - Assign next task only after previous completion - Ensure all agents work with consistent context - Maintain a single source of truth for specifications - Only request user confirmation when encountering significant architectural changes or blocking obstacles
10. Cleanup Phase: Perform comprehensive cleanup: - Remove any temporary files or code created during the process - Delete obsolete code that was replaced during implementation - Remove unused imports and dependencies - Clean up debug logs and comments that are no longer needed - Ensure no leftover development artifacts remain in the codebase
11. Upon completion of all tasks, commit with descriptive message and push changes to repository.Implementation
After several iterations, the spec is ready. I ask Qwen Code to implement the feature, strictly following the spec.
During the process, it will ask for permissions such as create files, execute commands, or build the project and so on. You can approve these requests. Any errors that occur are captured and fixed automatically. This saves a lot of time compared to when I used Zed for development.
sometimes, it may distract from the spec, you still need to stop it, ask to stickly follow your spec.
Debugging
Sometimes, the implementation and build process succeed, but when installed on the phone, the app crashes. In that case, I post the crash log, and the AI analyzes and fixes it.
adb logcat | grep ankihelperThis command retrieves logs from the application.
also we can start the app from adb
adb shell am start -n com.mmjang.ankihelper/.ui.LauncherActivitythis will start the laucher activity of the application.
It’s often helpful to ask the AI to add more debug logs to identify problems. Adding more log.d() statements in the code helps:
log.d("the response of the function");using adb to show the memory leak when build and deployed app is a debug app
adb logcat -s LeakCanary:*Takeaways
Here’s what I learned from the process:
- Communication is key. Make sure the AI fully understands your requirements and creates an executable spec.
- Have a clear blueprint for the feature. If your vision is ambiguous, the implementation will likely fail.
After updating AnkiHelper, I tried to use the same approach to integrate Marp presentations into Astro. I wanted to create an integration to convert Marp Markdown presentations to html and served in astro project, but after several rounds, I still couldn’t succeed. This was because I didn’t fully understand Astro’s internal build pipeline, including collections and integrations.
Today, I used Gemini Guided Learning to try to understand the process and key points of Astro integration. Maybe I’ll find a new angle to create a separate spec and try again. Using what I learned from Gemini Guided Learning, I’ve updated my site to better handle Marp presentations.
Tools
-
CodeRabbit CLI
-
install
Terminal window curl -fsSL https://cli.coderabbit.ai/install.sh | shthen execute to login to get authenticate token
-
use it
- with claude
Terminal window implement the tasks and run `coderabbit --prompt-only`, let it run as long as it needs (run it in the background) and fix any issues. - or use it separately in a code base by simply run
Terminal window coderabbit
- with claude
-
-
spec-kit: Toolkit to help you get started with Spec-Driven Development,
here is the steps to use it
-
install uv
Terminal window curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | bash -
install specify with uv
Terminal window uv tool install specify-cli --from git+https://github.com/github/spec-kit.git -
install and initialize
Terminal window specify init my-project --ai claude --script shor initialize in the current directory
Terminal window specify init --here --ai claude --script sh -
ask llm to fill the constitution
Terminal window /constitution fill the constitution wiwth the basre minumun requirement for <xxxx app> based on the template -
create the spec
Terminal window /specify <description of the requirement, not the technical details> -
create plan from the spec
Terminal window /plan <add some technical requirements, ask it to create the plans> -
breakdown the plan to tasks
Terminal window /tasks break down the plan to tasks -
implement, work with
coderabbitTerminal window /implement implement the tasks one by one and run `coderabbit --prompt-only`, let it run as long as it needs (run it in the background) and fix any issues.
-
-
openspec: Toolkit to help you get started with Spec-Driven Development,
- init openspec in your project
Terminal window $ openspec init - draft a proposal via
/openspec:proposal add <new feature> - check and review what openspec creates
Terminal window $ openspec list # Confirm the change folder exists$ openspec validate <new feature> # Validate spec formatting$ openspec show <new feature> # Review proposal, tasks, and spec delta - Refine the Specs, if required
- Implement the Change via
/openspec:apply <new feature>
- init openspec in your project
-
Hooks
-
https://github.com/diet103/claude-code-infrastructure-showcase
-
pre-compact Hooks
each time, when the context window is full, claude will auto compact the session, so some info will be lost, so i created a pre-compact hook to save the memory and thread when this event happend
-
add hooks config in ~/.claude/settings.json
"hooks": {"PreCompact": [{"hooks": [{"type": "command","command": "node $CLAUDE_HOME/hooks/pre-compact.js"}]}]} -
save the hook at
~/.claude/hooks/pre-compact.jsthis hook uses mcporter to call
Appendix
- config for linux to limit resource usage
- /etc/systemd/system/user@1001.service.d/override.conf
[Service]User=jenningslSlice=user-10001.sliceDelegate=pids memory cpu cpuset io
- /etc/systemd/system/user-1001.slice.d/override.conf
[Unit]Description=Resource limits for user jenningslDefaultDependencies=noBefore=slices.targetRequires=-.sliceAfter=-.slice[Slice]MemoryAccounting=trueMemoryHigh=75%MemoryMax=85%IOAccounting=trueIOReadBandwidthMax=/dev/vda 70MIOWriteBandwidthMax=/dev/vda 80MCPUQuota=150%AllowedCPUs=0-1
- /etc/systemd/system/user@1001.service.d/override.conf